7.6. Merge sort¶
We now turn our attention to using a divide and conquer strategy as a
way to improve the performance of sorting algorithms. The first
algorithm we will study is the merge sort. Merge sort is a recursive
algorithm that continually splits a vector in half. If the vector is empty
or has one item, it is sorted by definition (the base case). If the vector
has more than one item, we split the vector and recursively invoke a merge
sort on both halves. Once the two halves are sorted, the fundamental
operation, called a merge, is performed. Merging is the process of
taking two smaller sorted vectors and combining them together into a
single, sorted, new vector. Figure 10 shows our familiar example
vector as it is being split by mergeSort. Figure 11 shows
the simple vectors, now sorted, as they are merged back together.
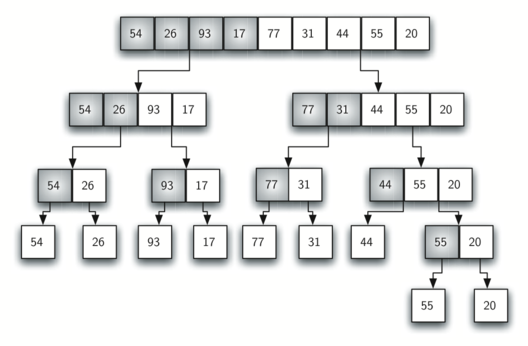
Figure 10: Splitting the vector in a Merge Sort¶
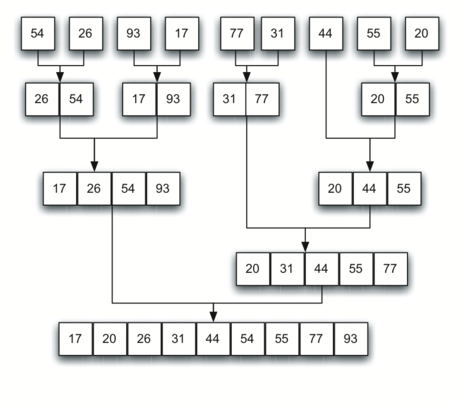
Figure 11: vectors as They Are Merged Together¶
The merge_sort function begins by checking the base case.
If the length of the vector is less than or equal to one,
then we already have a sorted vector and no more processing is needed.
If the length is greater than one,
then we extract the left and right halves.
It is important to note that the vector may not have an even
number of items. That does not matter, as the lengths will differ by at
most one.
Once the merge_sort function is invoked on the left half and the
right half (lines 23–24), it is assumed they are sorted. The rest of the
function is responsible for merging the two smaller sorted
vectors into a larger sorted vector. Notice that the merge operation places
the items back into the original vector (data) one at a time by
repeatedly taking the smallest item from the sorted vectors.
The print function shows the vector contents at the start of each invocation. There is also a print call at the end to show the merging process. The output shows the result of executing the function on our example vector.
Note that the vector with 44, 55, and 20 will not divide evenly. The first split gives [44] and the second gives [55,20]. It is easy to see how the splitting process eventually yields a vector that can be immediately merged with other sorted vectors.
In the following animation, red bars represent the element being looked at and blue represents the last element to look at during a pass.
In order to analyze the merge_sort function, we need to consider the
two distinct processes that make up its implementation.
First, the vector is split into halves.
We already computed (in a binary search) that we can divide a vector in half
\(\log n\) times where n is the length of the vector.
The second process is the merge.
Each item in the vector will eventually be processed and
placed on the sorted vector.
So the merge operation which results in a vector of size n requires n
operations.
The result of this analysis is that \(\log n\) splits,
each of which costs \(n\) for a total of \(n\log n\) operations.
A merge sort is an \(O(n \cdot log n)\) algorithm and even better,
it is also \(\Omega(n \cdot log n)\) in the worst case.
Recall that the slicing operator is \(O(k)\) where k is the size
of the slice. In order to guarantee that merge_sort will be
\(O(n \cdot log n)\) we will need to remove the slice operator. Again,
this is possible if we simply pass the starting and ending indices along
with the vector when we make the recursive call. We leave this as an
exercise.
It is important to notice that the merge_sort function requires extra
space to hold the two halves as they are extracted with the slicing
operations. This additional space can be a critical factor if the vector
is large and can make this sort problematic when working on large data sets.
Self Check
- [16, 49, 39, 27, 43, 34, 46, 40]
- This is the second half of the list.
- [21,1]
- Yes, mergesort will continue to recursively move toward the beginning of the list until it hits a base case.
- [21, 1, 26, 45]
- Remember mergesort doesn't work on the right half of the list until the left half is completely sorted.
- [21]
- This is the list after 4 recursive calls
sc-1-3: Given the following list of numbers: [21, 1, 26, 45, 29, 28, 2, 9, 16, 49, 39, 27, 43, 34, 46, 40] which answer illustrates the list to be sorted after 3 recursive calls to mergesort?
- [21, 1] and [26, 45]
- The first two lists merged will be base case lists, we have not yet reached a base case.
- [[1, 2, 9, 21, 26, 28, 29, 45] and [16, 27, 34, 39, 40, 43, 46, 49]
- These will be the last two lists merged
- [21] and [1]
- The lists [21] and [1] are the first two base cases encountered by mergesort and will therefore be the first two lists merged.
- [9] and [16]
- Although 9 and 16 are next to each other they are in different halves of the list starting with the first split.
sc-1-4: Given the following list of numbers: [21, 1, 26, 45, 29, 28, 2, 9, 16, 49, 39, 27, 43, 34, 46, 40] which answer illustrates the first two lists to be merged?
More to Explore
TBD